Important Questions
1. Draw the structure of hex-l-en-3-ol compound.
2. What happens when ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH?
3. How will you convert the following?
(i) Propan-2-ol to propanone.
(ii) Phenol to 2,4,6 – tribromophenol?
4. Explain the following giving one example for each:
1. Reimer-Tieman reaction.
2. Friedel Craft’s acetylation of anisole.
5. How would you obtain:
(i) Picric acid (2, 4, 6-Trinitrophenol) from phenol.
(ii) 2-Methylpropene from 2-methylpropanol?
6. Draw the structure and name the product formed if the following alcohols are oxidized.
Assume that an excess of oxidizing agent is used.
(i) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
(ii) 2-butenol
(iii) 2-methyl-l-propanol
Sample Questions
1. Draw the structure and name the product formed if the following alcohols are oxidized.
Assume that an excess of oxidizing agent is used.
(i) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
(ii) But-1-en-2-ol
(iii) 2-methyl-l-propanol
2. How will you convert:
(i) Propene to Propan- 1-ol?
(ii) Ethanal to Propan-2-ol?
3. Name the reagents which are used in the following conversions:
(i) A primary alcohol to an aldehyde
(ii) Butan -2 - one to butan-2-ol
(iii) Phenol to 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol
4. Explain the following observations:
i. The boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of methoxymethane.
ii. Phenol is more acidic than ethanol.
iii. o- and p- nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol.
5. Write the equations involved in the following reactions:
(i) Reimer – Tiemann reaction
(ii) Williamson synthesis
6. How do you convert the following:
Ethanol to Propanone
7. Illustrate the following reactions giving a chemical equation for each:
(i) Kolbe’s reaction.
(ii) Williamson synthesis.
8. (a) Identify the chiral molecule in the following pair?
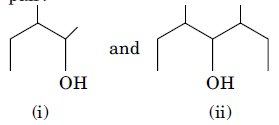
(b) Write the structure of the product when chlorobenzene is treated with methyl chloride in the presence of sodium metal and dry ether.
(c) Write the structure of the alkene formed by dehydrohalogenation of 1-bromo-1-methylcyclohexane with alcoholic KOH.




