Important Questions
1. Draw the structure of 4-chloropentan-2-one.
2. Draw the structure of 3-methylbutanal.
3. Write the structural formula of 1-phenylpentan-1-one.
4. Draw the structural formula of 1-phenylpropan-1-one molecule.
5. (a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between:
(i) Propanal and propanone
(ii)Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
(b) How would obtain:
(i) But-2-enal from ethanol.
(ii)Butanoic acid from butanol
(iii)Benzoic acid from ethylbenzene
Sample Questions
1. (a) Illustrate the following name reactions:
Assume that an excess of oxidizing agent is used.
(i) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(ii) Clemmensen reduction
(b) How would you obtain the following:
(i) But-2-enal from ethanal
(ii) Butanoic acid from butanol
(iii) Benzoic acid from ethylbenzene
OR
(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following:
(i) Benzoic acid and ethyl benzoate
(ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
(b) Complete each synthesis by giving missing reagents or products in the following:
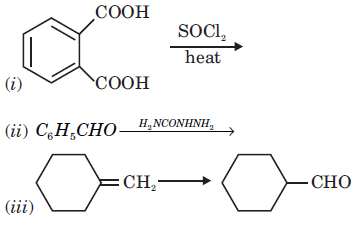
2. (a) Complete the following reaction statements by giving the missing starting material, reagent or product as required:
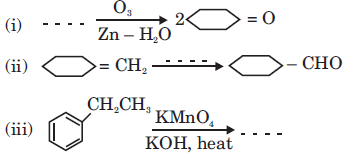
(b) Describe the following reactions:
(i) Cannizaro reaction
(ii) Cross aldol condensation
OR
(a) How would you account for the following?
(i) Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones towards nucleophiles.
(ii) The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are lower than of the
corresponding acids.
(iii) The aldehydes and ketones undergo a number of addition reactions.
(b) Give chemical tests to distinguish between:
(i) Acetaldehyde and benzaldehyde
(ii) Propanone and propanol
3. (a) Explain the mechanism of a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl group of an aldehyde or a ketone.
(b) An organic compound (A) (molecular formula C8H16O2) was hydrolyse with dilute sulphuric acid to give a carboxylic acid (B) and an alcohol (C). Oxidation of (C) with chromic acid also produced (B). On dehydration (C) gives but-1- ene. Write the equations for the reactions involved.
OR
(a) Given chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Ethanal and Propanal
(b) How will you bring about the following conversions?
(i) Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde
(ii) Ethanal to but-2-enal
(iii) Propanone to propene
Give complete reaction in each case.
4. Write the structure of 2-hydroxybenzoic acid.
5. How do you convert the following?
Toluene to benzoic acid
OR
Account for the following:
(a) Aromatic carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
(b) pKa value of 4-nitrobenzoic acid is lower than that of benzoic acid.





