Important Questions
1. Which one of PCl4+ and PCl4– is not likely to exist and why?
2. Why does NH3 act as a Lewis base?
3. Write the formulae of any two oxo-acids of phosphorus.
4. In which one of the two structures, NO2+ and NO2–, the bond angle has a higher value?
5. Why is red phosphorus less reactive than white phosphorus?
6. (a) What type of semiconductor is obtained when silicon is doped with boron?
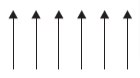
(b) What type of magnetism is shown in the following alignment of magnetic moments?
(c) What type of point defect is produced when AgCl is doped with CdCl2?
7. Given reasons for the following:
(i) (CH3)3P = O exists but (CH3)3 N = O does not.
(ii) Oxygen has less electron gain enthalpy with negative sign than sulphur.
(iii) H3PO2 is a stronger reducing agent than H3PO3.
8. Give reasons for the following:
(a) Red phosphorus is less reactive than white phosphorus.
(b) Electron gain enthalpies of halogens are largely negative.
(c) N2O5 is more acidic than N2O3.
9. Draw the structures of the following molecules:
(i) (HP3 )3 HPO
(ii) BrF3
Sample Questions
1. Account for the following:
(i) Sulphur in vapour form exhibit paramagnetic behaviour.
(ii) SnCl4 is more covalent than SnCl2.
(iii) H3PO2 is stronger reducing agent than H3PO3.
2. Draw the structure of BrF3 molecule.
3. Explain the following giving an appropriate reason in each case.
(i) O2 and F2 both stabilize higher oxidation states of metals but O2 exceeds F2 in doing so.
(ii) Structures of Xenon fluorides cannot be explained by Valence Bond approach.
4. What happens when
(i) PCl5 is heated?
(ii) H3PO3 is heated?
Write the reaction involved.
5. How are inter-halogen compounds formed? What general compositions can be assigned to them?
6. Account for the following:
(i) PCl5 is more covalent than PCl3.
(ii) Iron on reaction with HCl forms FeCl2 and not FeCl3.
(iii) The two O-O bond lengths in the ozone molecule are equal.
7. Write chemical equations for the following processes:
(i) Chlorine reacts with a hot concentrated solution of sodium hydroxide.
(ii) Ortho phosphorous acid is heated
(iii) PtF6 and xenon are mixed together
8. Explain the following:
(i) NF3 is an exothermic compound whereas NCl3 is not.
(ii) F2 is most reactive of all the four common halogens.
9. (a) What happens when
(i) chlorine gas is passed through a hot concentrated solution of NaOH?
(ii) sulphur dioxide gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a Fe (III) salt?
(b) Answer the following:
(i) What is the basicity of H3PO3 and why?
(ii) Why does fluorine not play the role of a central atom in inter halogen compounds?
(iii) Why do noble gases have very low boiling points?
10. (a) Give reasons for the following:
(i) Bond enthalpy of F2 is lower than that of Cl2.
(ii) PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3.
(b) Draw the structures of the following molecules:
(i) BrF3
(ii) (HPO3)3
(iii) XeF4
OR
(a) Account for the following:
(i) Helium is used in diving apparatus.
(ii) Flourine does not exhibit positive oxidation state.
(iii) Oxygen shows catenation behaviour less than sulphur.
(b) Draw the structures of the following molecules.
(i) XeF2
(ii) H2S2O8
11. Draw the structures of the following molecules:
(i) XeF6
(ii) H2S2O7




