Important Questions
1. Define the term ‘Mobility’ of charge carriers in a conductor. Write its S.I. unit.
2. Show variation of resistivity of copper as a function of temperature in a graph.
3. Nichrome and copper wires of same length and same radius are connected in series. Current I is passed through them. Which wire gets heated up more? Justify your answer.
4. Explain the term ‘drift velocity’ of electrons in a conductor. Hence obtain the expression for the current through a conductor in terms of ‘drift velocity’.
5. Estimate the average drift speed of conduction electrons in a copper wire of cross-sectional area 2.5 × 10–7 m2 carrying a current of 2.7 A. Assume the density of conduction electrons to be 9 × 1028 m–3.
6. When 5V potential difference is applied across a wire of length 0.1 m, the drift speed of electrons is 2.5 × 10–4 m/s. If the electron density in the wire is 8 × 1028 m–3, calculate the resistivity of the material of wire.
7. A potential difference V is applied across a conductor of length L and diameter D. How is the drift velocity, v1 of charge carriers in the conductor affected when (i) V is halved, (ii) L is doubled and (iii) D is halved? Justify your answer in each case.
8. Define the terms (i) drift velocity, (ii) relaxation time. A conductor of length L is connected to a dc source of emf 8. If this conductor is replaced by another conductor of same material and same area of cross-section but of length 3L, how will the drift velocity change?
9. Derive an expression for drift velocity of free electrons in a conductor in terms of relaxation time.
10. (a) Define the term ‘conductivity’ of a metallic wire. Write its SI unit.
(b) Using the concept of free electrons in a conductor, derive the expression for the conductivity of a wire in terms of number density and relaxation time. Hence obtain the relation between current density and the applied electric field E.
Sample Questions
1. A cell of emf E and internal resistance r is connected to two external resistances R1 and and R2 a perfect ammeter. The current in the circuit is measured in four different situations:
(i) without any external resistance in the circuit
(ii) with resistance R1 only
(iii) with R1 and R2 in series combination
(iv) with R1 and R2 in parallel combination
The currents measured in the four cases are 0.42 A, 1.05 A, 1.4 A and 4.2 A, but not necessarily in that order. Identify the currents corresponding to the four cases mentioned above.
2. An ammeter of resistance 1 Ω can measure current up to 1.0 A.
What must be the value of the shunt resistance to enable the ammeter to measure up to 5.0 A?
(ii) What is the combined resistance of the ammeter and the shunt?
3. A 10 V battery of negligible internal resistance is connected across a 200 V battery and a resistance of 38Ω as shown in the figure. Find the value of the current in circuit.
4. A cell of emf ‘E’ and internal resistance is connected across a variable resistor ‘R’. Plot a graph showing the variation of terminal potential ‘V’ with resistance ‘R’. Predict from the graph the condition under which ‘V’ becomes equal to ‘E’.
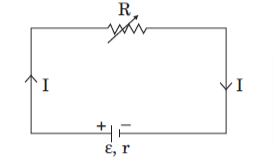
5. A variable resistor R is connected across a cell of emf ε and internal resistance r as shown in the figure. Draw a plot showing the variation of:
(i) Terminal voltage V
(ii) the current I, as a function of R.
6. State Kirchhoff’s rules. Explain briefly how these rules are justified.
7. An ammeter of resistance 0.80 Ω can measure current up to 1.0 A.
(i) What must be the value of shunt resistance to enable the ammeter to measure current up to 5.0 A?
(ii) What is the combined resistance of the ammeter and the shunt?
8. In the given circuit diagram a voltmeter ‘V’ is connected across a lamp ‘L’. How would (i) the brightness of the lamp and (ii) voltmeter reading ‘V’ be affected, if the value of resistance ‘R’ is decreased? Justify your answer.
9. Two cell of emfs 1.5 V and 2.0 V having internal resistances 0.2 Ω and 0.3 Ω respectively are connected in parallel. Calculate the emf and internal resistance of the equivalent cell.
10. State Kirchhoff’s rules for an electric network. Using Kirchhoff’s rules, obtain the balance condition in terms of the resistance of four arms of Wheatstone bridge.




