Chapter 6: Electromagnetic Induction
Important Questions
1. The motion of copper plates is damped when it is allowed to oscillate between the two poles of a magnet. If slots are cut in the plate, how will the damping be affected?
2. Two spherical bobs, one metallic and the other of glass, of the same size are allowed to fall freely from the same height above the ground. Which of the two would reach earlier and why?
3. A planar loop of rectangular shape is moved within the region of a uniform magnetic field acting perpendicular to its plane. What is the direction and magnitude of the current induced in it?
4. A metallic rod of ‘L’ length is rotated with angular frequency of ω with one end hinged at the centre and the other end at the circumference of a circular metallic ring of radius L about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the ring. A constant and uniform magnetic field B parallel to the axis is present everywhere. Deduce the expression for the emf between the centre and the metallic ring.
5. While travelling back to his residence in the car, Dr. Pathak was caught up in a thunderstorm. It became very dark. He stopped driving the car and waited for thunderstorm to stop. Suddenly he noticed a child walking alone on the road. He asked the boy to come inside the car till the hunderstorm stopped. Dr. Pathak dropped the boy at his residence. The boy insisted that Dr. Pathak should meet his parents. The parents expressed their gratitude to Dr. Pathak for his concern for safety of the child.
Answer the following questions based on the above information:
(a) Why is it safer to sit inside a car during a thunderstorm?
(b) Which two values are displayed by Dr. Pathak in his action?
(c) Which values are reflected in parent’s response to Dr. Pathak?
(d) Give an example of similar action on your part in the part from everyday life.
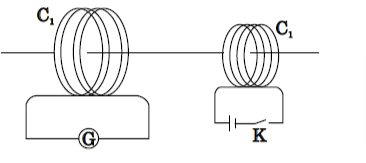
6. A current is in induced in coil C1 due to the motion of current carrying coil C2.
(a) Write any two ways by which a large deflection can be obtained in the galvanometer G,
(b) Suggest an alternative device to demonstrate the induced current in place
of a galvanometer.