Chapter 4: Moving Charges & Magnetism
Important Questions
1. (a) State Biot – Savart law and express this law in the vector form.
(b) Two identical circular coils, P and Q each of radius R, carrying currents 1A and √3 A respectively, are placed concentrically and perpendicular to each other lying in the XY and YZ planes. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at the centre of the coils.
2. (a) State Ampere’s Circuital law, expressing it in the integral form.
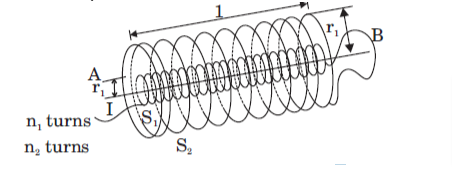
(b) Two long coaxial insulated solenoids, S1 and S2 of equal lengths are wound one over the other as shown in the figure. A steady current “I” flows through the inner solenoid S1 to the other end B, which is connected to the outer solenoid S2 through which the same current “I” flows in the opposite direction so as to come out at end A. If n1 and n2 are the number of turns per unit length, find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at a point (i) inside on the axis and (ii) outside the combined system.
3. A long straight wire of a circular cross-section of radius ‘a’ carries a steady current ‘I’. The current is uniformly distributed across the cross-section.
Apply Ampere’s circuital law to calculate the magnetic field at a point ‘r’ in the region for
(i) r < a and (ii) r > a.
4. State Biot-Savart law, giving the mathematical expression for it. Use this law to derive the expression for the magnetic field due to a circular coil carrying current at a point along its axis. How does a circular loop carrying current behave as a magnet?
5. State the underlying principle of a cyclotron. Write briefly how this machine is used to accelerate charged particles to high energies.



