Important Questions
1. Under what condition does a biconvex lens of glass having a certain refractive index act as a plane glass sheet when immersed in a liquid?
2. Write the relationship between angle of incidence ‘i’, angle of prism ‘A’ and angle of minimum deviations Δm for a triangular prism.
3. A convex lens of focal length 25 m is placed co axially in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm. Determine the power of the combination. Will the system be converging or diverging in nature?
4. A convex lens of focal length f1 is kept in contact with a concave lens of focal length f2. Find the focal length of the combination.
5. A convex lens of focal length 30 cm is placed coaxially in contact with a concave lens of focal length 40 cm. Determine the power of the combination. Will the system be converging or diverging in nature?
Sample Questions
1. (a) Calculate the distance of an object of height h from a concave mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm, so as to obtain a real image of magnification 2. Find the location of image.
(b) Using mirror formula, explain why a convex mirror always produces a virtual image.
2. (i) A screen is placed at a distance of 100 cm from an object. The image of the object is formed on the screen by a convex lens for two different location of the lens separated by 20 cm. Calculate the focal length of the lens used.
(ii) A converging lens is kept coaxially in contact with a diverging lens-both the lenses being of equal focal length. What is the focal length of the combination?
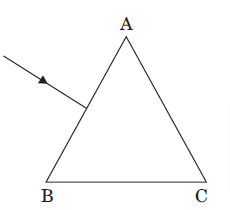
3. The figure shows a ray of light falling normally on the face AB of an equilateral glass prism having refractive index 3/2, placed in water of refractive index 4/3. Will this ray suffer total internal reflection on striking the face AC?
Justify your answer.
4. (a) A point-object is placed on the principal axis of convex spherical surface of radius of curvature R, which separates the two media of refractive indices n1 and n2 (n2 > n1). Draw the ray diagram and deduce the relation between the distance of the object (u), distance of the image (v) and the radius of curvature (R for refraction to take place at the convex spherical surface from rarer to denser medium.
(b) Use the above relation to obtain the condition on the position of the object and the radius of curvature in terms of n1 and n2 when the real image is formed.
5. (a) Draw a ray diagram to show image formation when the concave mirror produces a real, inverted and magnified image of the object.
(b) Obtain the mirror formula and write the expression for the linear magnification.
(c) Explain two advantages of a reflecting telescope over a refracting telescope.




